#TheBodyPhysiology: The Physiology Of Hearing
Nigeria
0
✒️ - By Aan Gray
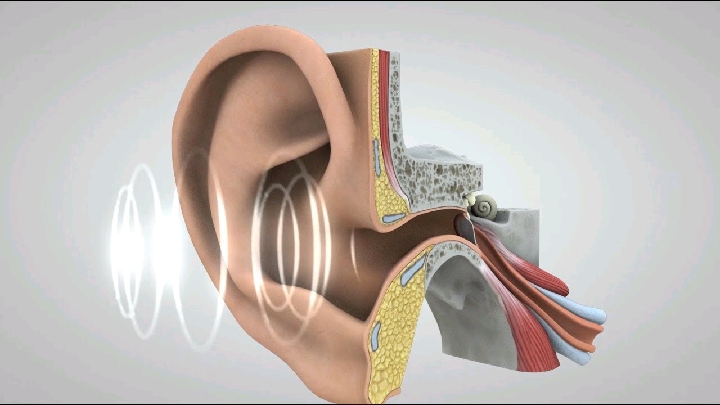
 Every sound produce sound waves or vibrations in the air, which travel at about 332 metre per second. The auricle, because of its shape, collects and concentrates the waves and directs them along the auditory canal causing the tympanic membrane to vibrate. Tympanic membrane vibrations are transmitted and amplified through the middle ear by movement of the ossicles. At their medial end the footplate of the stapes rocks to and fro in the oval window, setting up fluid waves in the perilymph of the scala vestibuli. Some of the force of these waves is transmitted along the length of the scala vestibuli and scala tympani, but most of the pressure is transmitted into the cochlear duct. This causes a corresponding wave motion in the endolymph, resulting in vibration of the basilar membrane and stimulation of the auditory receptors in the hair cells of the spiral organ. The nerve impulses generated pass to the brain in the cochlear (auditory) portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (8th cranial nerve). The fluid wave is finally expended into the middle ear by vibration of the membrane of the round window. The vestibulocochlear nerve transmits the impulses to the auditory nuclei in the medulla, where they synapse before they are conducted to the auditory area in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum. Because some fibres cross over in the medulla and others remain on the same side, the left and right auditory areas of the cerebrum receive impulses from both ears.
Every sound produce sound waves or vibrations in the air, which travel at about 332 metre per second. The auricle, because of its shape, collects and concentrates the waves and directs them along the auditory canal causing the tympanic membrane to vibrate. Tympanic membrane vibrations are transmitted and amplified through the middle ear by movement of the ossicles. At their medial end the footplate of the stapes rocks to and fro in the oval window, setting up fluid waves in the perilymph of the scala vestibuli. Some of the force of these waves is transmitted along the length of the scala vestibuli and scala tympani, but most of the pressure is transmitted into the cochlear duct. This causes a corresponding wave motion in the endolymph, resulting in vibration of the basilar membrane and stimulation of the auditory receptors in the hair cells of the spiral organ. The nerve impulses generated pass to the brain in the cochlear (auditory) portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (8th cranial nerve). The fluid wave is finally expended into the middle ear by vibration of the membrane of the round window. The vestibulocochlear nerve transmits the impulses to the auditory nuclei in the medulla, where they synapse before they are conducted to the auditory area in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum. Because some fibres cross over in the medulla and others remain on the same side, the left and right auditory areas of the cerebrum receive impulses from both ears.
 Sound waves have the properties of pitch and volume, or intensity. Pitch is determined by the frequency of the sound waves and is measured in Hertz (Hz). Sounds of different frequencies stimulate the basilar membrane at different places along its length, allowing discrimination of pitch. The volume depends on the magnitude of the sound waves and is measured in decibels (dB). The greater the amplitude of the wave created in the endolymph, the greater is the stimulation of the auditory receptors in the hair cells in the spiral organ, enabling perception of volume. Long-term exposure to excessive noise causes hearing loss because it damages the sensitive hair cells of the spiral organ.
Sound waves have the properties of pitch and volume, or intensity. Pitch is determined by the frequency of the sound waves and is measured in Hertz (Hz). Sounds of different frequencies stimulate the basilar membrane at different places along its length, allowing discrimination of pitch. The volume depends on the magnitude of the sound waves and is measured in decibels (dB). The greater the amplitude of the wave created in the endolymph, the greater is the stimulation of the auditory receptors in the hair cells in the spiral organ, enabling perception of volume. Long-term exposure to excessive noise causes hearing loss because it damages the sensitive hair cells of the spiral organ.
 Tags: #ScienceWithGray #ScienceOnBuzz #TheBodyPhysiology #Science
Tags: #ScienceWithGray #ScienceOnBuzz #TheBodyPhysiology #Science
 Every sound produce sound waves or vibrations in the air, which travel at about 332 metre per second. The auricle, because of its shape, collects and concentrates the waves and directs them along the auditory canal causing the tympanic membrane to vibrate. Tympanic membrane vibrations are transmitted and amplified through the middle ear by movement of the ossicles. At their medial end the footplate of the stapes rocks to and fro in the oval window, setting up fluid waves in the perilymph of the scala vestibuli. Some of the force of these waves is transmitted along the length of the scala vestibuli and scala tympani, but most of the pressure is transmitted into the cochlear duct. This causes a corresponding wave motion in the endolymph, resulting in vibration of the basilar membrane and stimulation of the auditory receptors in the hair cells of the spiral organ. The nerve impulses generated pass to the brain in the cochlear (auditory) portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (8th cranial nerve). The fluid wave is finally expended into the middle ear by vibration of the membrane of the round window. The vestibulocochlear nerve transmits the impulses to the auditory nuclei in the medulla, where they synapse before they are conducted to the auditory area in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum. Because some fibres cross over in the medulla and others remain on the same side, the left and right auditory areas of the cerebrum receive impulses from both ears.
Every sound produce sound waves or vibrations in the air, which travel at about 332 metre per second. The auricle, because of its shape, collects and concentrates the waves and directs them along the auditory canal causing the tympanic membrane to vibrate. Tympanic membrane vibrations are transmitted and amplified through the middle ear by movement of the ossicles. At their medial end the footplate of the stapes rocks to and fro in the oval window, setting up fluid waves in the perilymph of the scala vestibuli. Some of the force of these waves is transmitted along the length of the scala vestibuli and scala tympani, but most of the pressure is transmitted into the cochlear duct. This causes a corresponding wave motion in the endolymph, resulting in vibration of the basilar membrane and stimulation of the auditory receptors in the hair cells of the spiral organ. The nerve impulses generated pass to the brain in the cochlear (auditory) portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (8th cranial nerve). The fluid wave is finally expended into the middle ear by vibration of the membrane of the round window. The vestibulocochlear nerve transmits the impulses to the auditory nuclei in the medulla, where they synapse before they are conducted to the auditory area in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum. Because some fibres cross over in the medulla and others remain on the same side, the left and right auditory areas of the cerebrum receive impulses from both ears. Sound waves have the properties of pitch and volume, or intensity. Pitch is determined by the frequency of the sound waves and is measured in Hertz (Hz). Sounds of different frequencies stimulate the basilar membrane at different places along its length, allowing discrimination of pitch. The volume depends on the magnitude of the sound waves and is measured in decibels (dB). The greater the amplitude of the wave created in the endolymph, the greater is the stimulation of the auditory receptors in the hair cells in the spiral organ, enabling perception of volume. Long-term exposure to excessive noise causes hearing loss because it damages the sensitive hair cells of the spiral organ.
Sound waves have the properties of pitch and volume, or intensity. Pitch is determined by the frequency of the sound waves and is measured in Hertz (Hz). Sounds of different frequencies stimulate the basilar membrane at different places along its length, allowing discrimination of pitch. The volume depends on the magnitude of the sound waves and is measured in decibels (dB). The greater the amplitude of the wave created in the endolymph, the greater is the stimulation of the auditory receptors in the hair cells in the spiral organ, enabling perception of volume. Long-term exposure to excessive noise causes hearing loss because it damages the sensitive hair cells of the spiral organ. Tags: #ScienceWithGray #ScienceOnBuzz #TheBodyPhysiology #Science
Tags: #ScienceWithGray #ScienceOnBuzz #TheBodyPhysiology #Science
Comments (0)
0/500
New Comments(0)
What do you think of this post?